This New Linux App Makes Android File Sharing a Breeze

Sharing files between Linux and Android has often been a complicated process involving unreliable Linux utilities or complex network configurations. A new application, Packet, aims to solve this problem by providing a single wireless file transfer solution. Let’s find out how!
What is the package and how it works
Packet is a Linux application that fits into the quick sharing function of Android (formerly nearby). It allows your Linux machine to be discoverable and to share files with Android phones, tablets and chromebooks nearby without requiring any additional application on your Android device.

Related
How to configure a quick sharing on Windows for pain transfers
Sharing files has never been faster or effortless!
The application works by implementing Google’s fast sharing protocol. It uses a combination of Bluetooth for discovery and your local Wi-Fi network for the transfer of real files. When you launch a sharing, the package diffuses its presence and your Android device recognizes it as a valid fast sharing target.
Unlike other solutions like KDE Connect, FTP servers or Cloud storage, Packet does not force you to install additional applications on your Android device or to play with network settings. Quick sharing is already integrated into most Android phones, so you are ready to get out of the box.

Related
Kde Connect arrives on iPhone and iPad for Linux fans
KDE Connect, a Linux PC phone connection tool, is finally available for iPhone and iPad.
On the Linux side, just install a package. You don’t need to create an account, subscribe to cloud storage or configure complex network settings – the Cacket is done directly. You install it, run it and start transferring files.
Installation of packages in Linux
The package is available as flatpak, which simplifies installation with most Linux systems. However, make sure you have Flatpak and the Flatpak repository configured on your system.

Related
What is a flatpak in Linux, and how to install one?
FlatPaks without required assembly.
Once Flatpak is configured, open a terminal and perform this:
flatpak install flathub io.github.nozwock.Packet
Confirm the installation when you are invited. Once the end of its end, you can find and start the package from the application menu for your system.
How to use the package to transfer files to Android
The package interface is minimal and simple for sending and receiving files. Before you start, make sure that Bluetooth is activated on your Android device and that the two devices are on the same Wi-Fi network. Also make sure that fast sharing is activated on your devices.
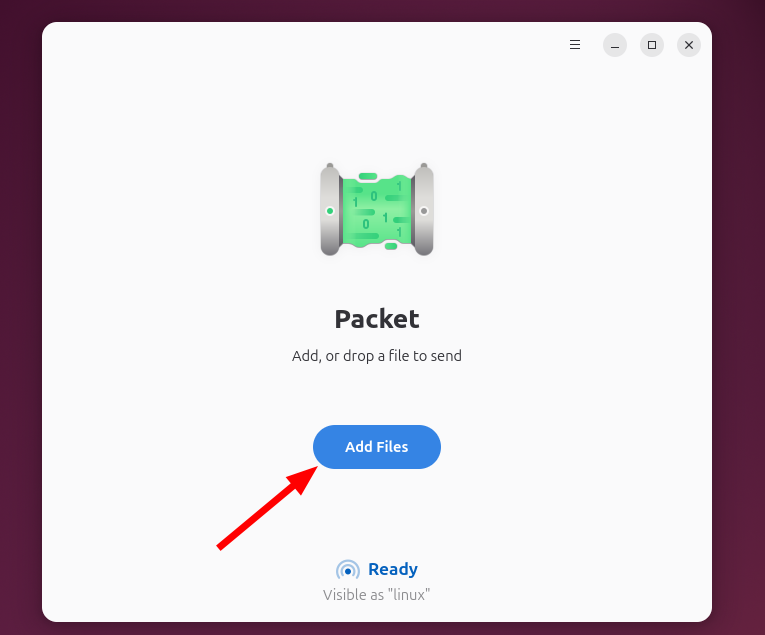
For example, to send Linux files to Android, launch a package on your Linux machine from the Applications menu. Then add files by pressing the Add files option or simply sliding them and placing them in the application window.
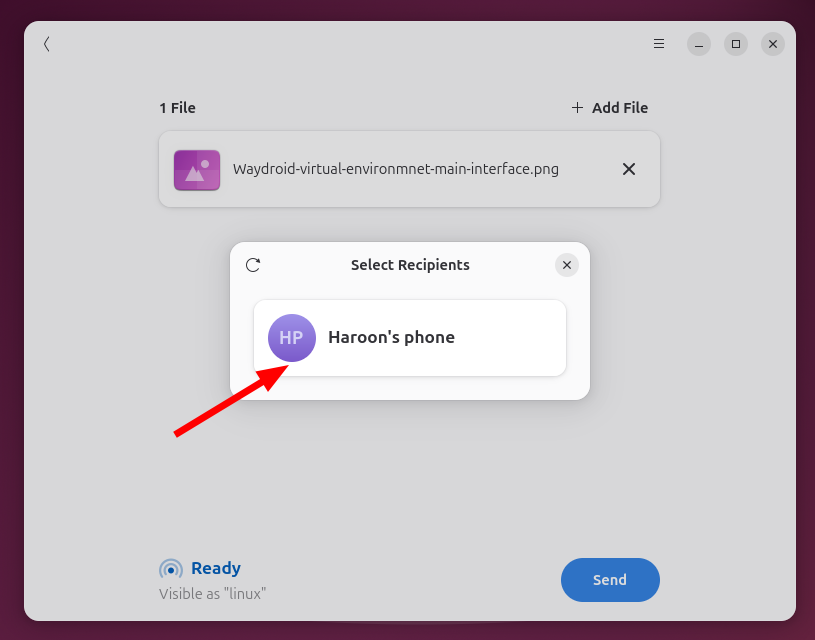
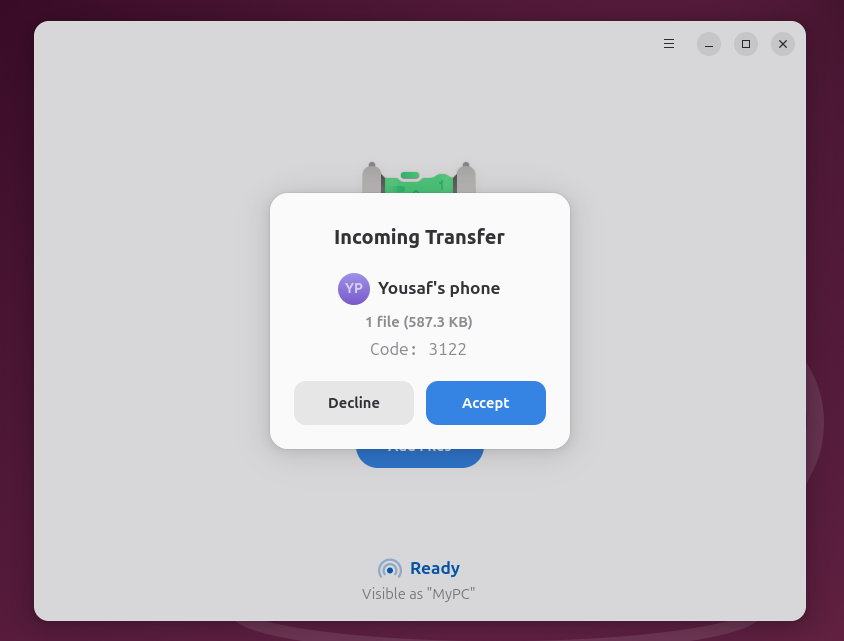
In the Packet window, click Send and select your Android device once it appears.
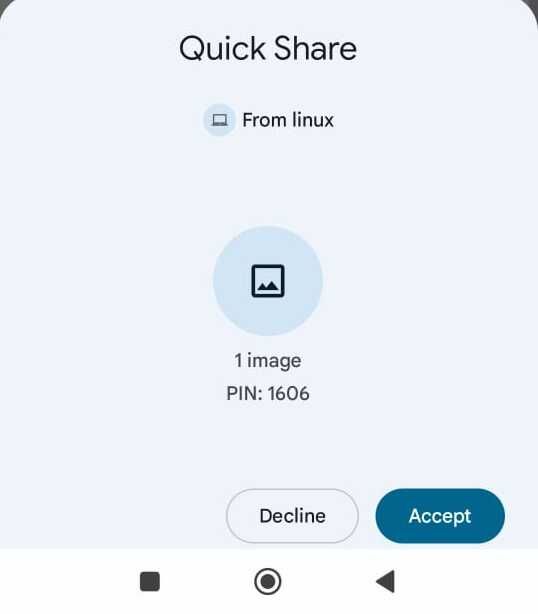
A notification will appear on your Android device. Type accept to start the transfer. The file will be delivered in the download folder of your device.
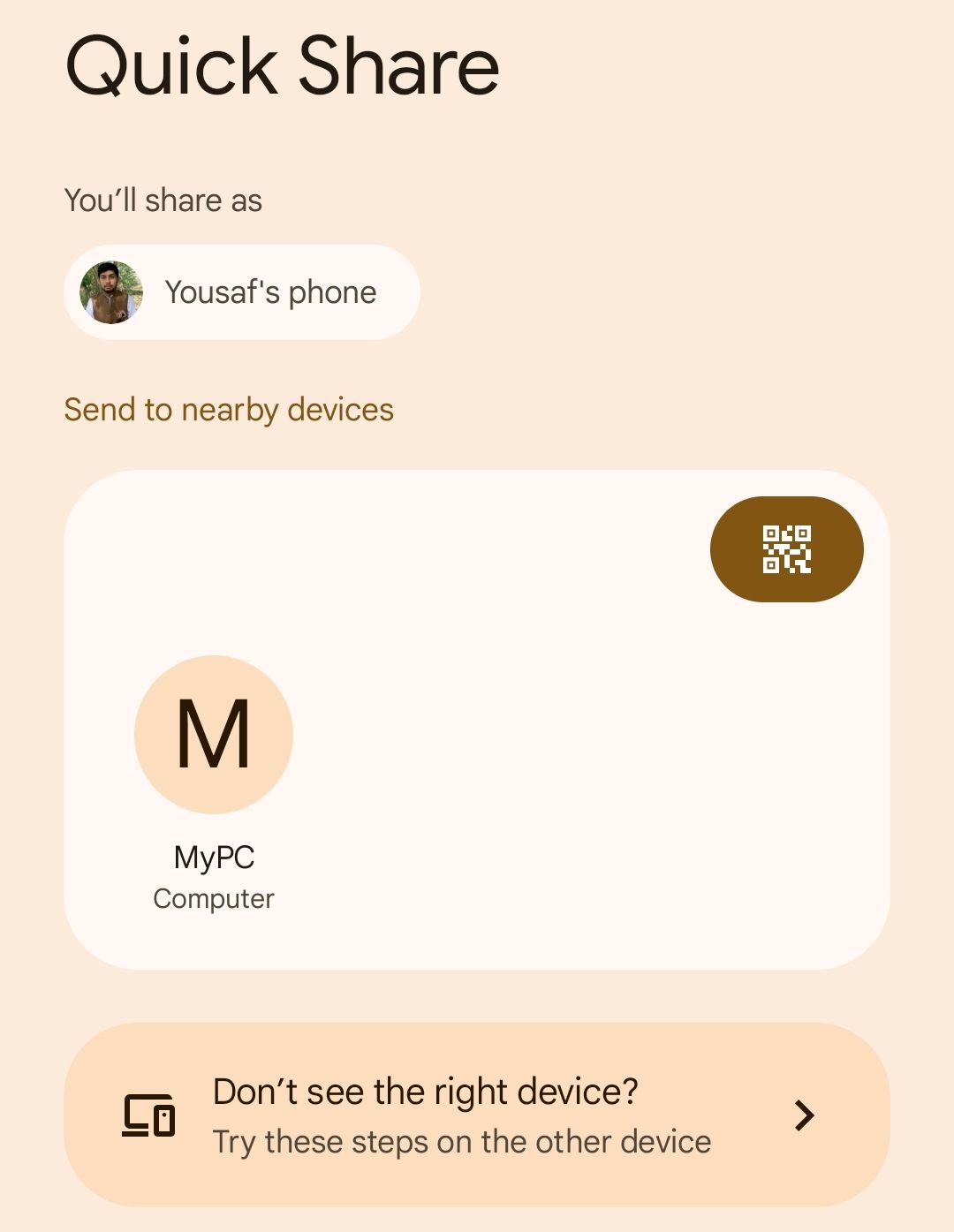
Similarly, to receive files on Linux from Android, open Packet on your Linux computer to make it discoverable. On your Android device, choose the file you plan to send and press the sharing icon. Then choose a quick sharing in sharing options. Your Linux machine must appear as a target. Press his name.
Finally, accept the transfer entering the Packet application. The file will be transferred directly to the download folder on your computer.
First impressions
Packet is an excellent application with a solid concept, but I have encountered some problems during tests, most of them linked to network connectivity.
For example, on my old Android device running Android 12, I was able to receive files from my PC, but I could not send phone files to the PC, because my PC did not appear in the quick sharing search results. As recommended by the developer, I also adjusted the firewall parameters of my system, but the PC has still not presented itself. On the other hand, on my new Android devices, sending and receiving files work perfectly without any problems.
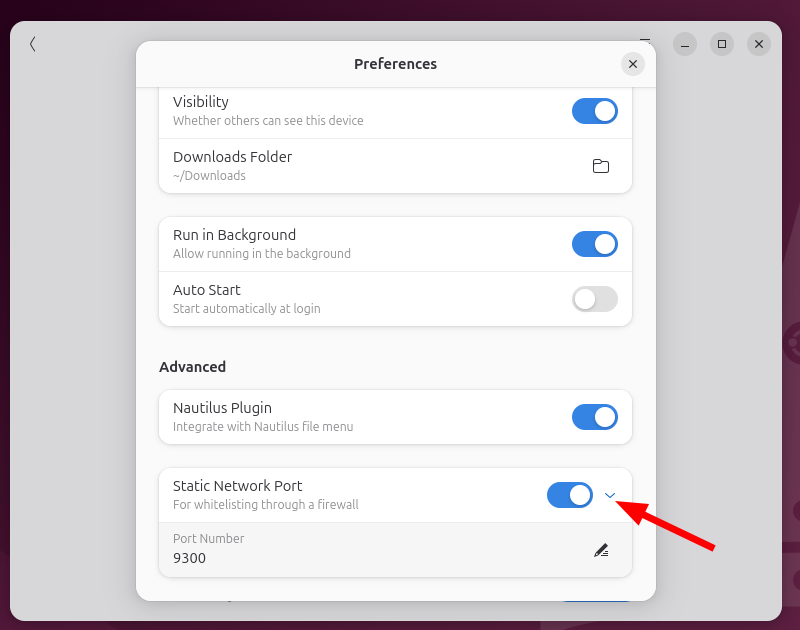
If you do not know how to activate the static Packet port option, it’s simple: open the preference menu (three horizontal lines), scroll down and switch the static network port on ON. Then make sure that Port 9300 is open to your firewall to allow transfers of smooth files.
The package only provides basic features, such as personalization of the device name, tilting visibility on or deactivating, definition of your download file and the execution of the package in the background with notifications when the transfers are completed. In some file managers, such as Nautilus, you can even right -click a file and send it directly using packages.
To use the Nautilus plugin, first install the required packages:
sudo apt install python3-dbus python3-nautilus
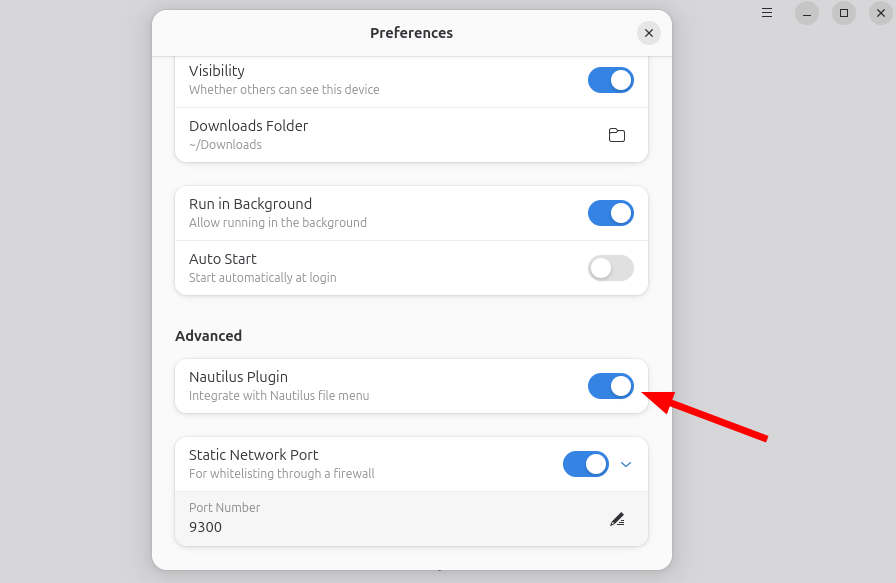
Then activate the Nautilus plugin from the Preferences tab.
If the integration does not work or does not show a missing directory error, you must create the repertoire required for the extensions of Nautilus Python with this:
mkdir -p ~/.local/share/nautilus-python/extensions
This repertoire is the place where Packet places its integration script to click with the right button on Nautilus.
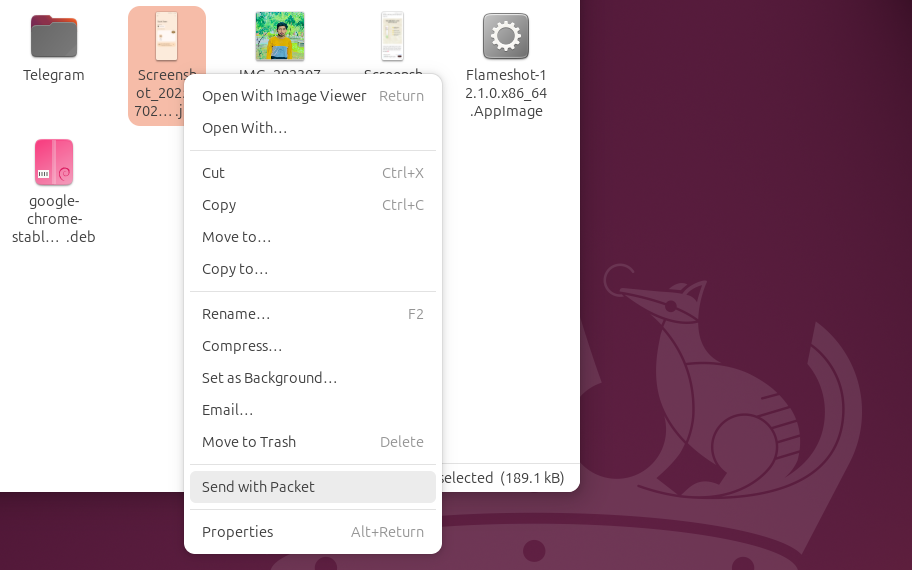
After creating the repertoire, log out and reconnect to your system. Then, open the Nautilus file manager, right -click on the file you want to send and choose send with Packet.
The package will then launch you and invite you to select the recipient. This deep integration makes file sharing between Linux and Android without seam and fast.
Try it. It is a good counter between KDE Connect and Localsend in terms of simplicity and power.